Installation
Install the CodeLogician VS Code extension from the Visual Studio Marketplace
Alternatively, install directly from the extension pane in VS Code.
Once installed, the extension will guide you through configuring your API key to get started. If this hasn't happened, refer to Configuration
ImandraX
For the full formal verification workflow, Imandra recommends installing the ImandraX extension. The ImandraX extension provides:
- IML Support: Full IDE support for IML (Imandra Modeling Language) files
- Theorem Prover: Automatically proves or disproves mathematical properties about your code
- Interactive Analysis: Explore formal models and proofs interactively
This enables you to verify the formal models and verification goals generated by CodeLogician.
Basic Usage
Supported languages
CodeLogician supports the following languages:
- Python
- C#
- Rust
- Java
- Kotlin
- TypeScript
- JavaScript
- Go
- Ruby
- Dart
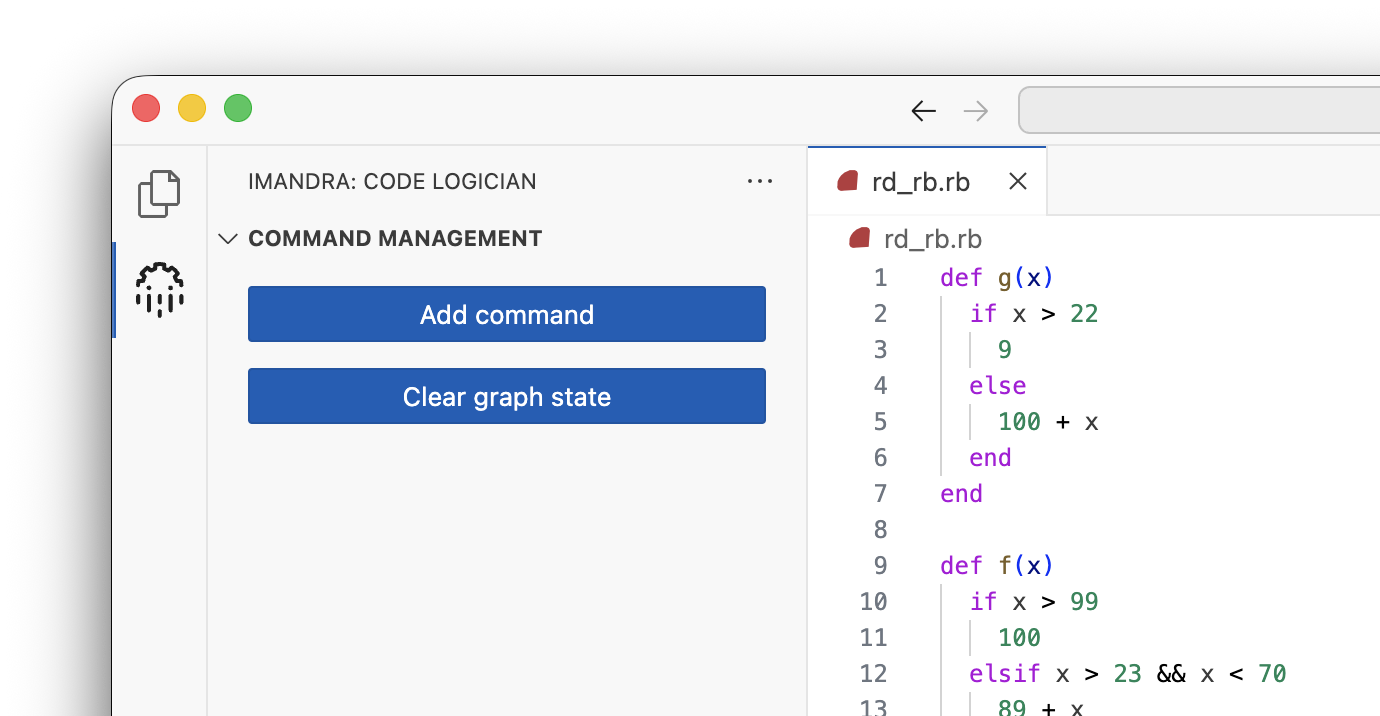
To begin, open a source file. Then open the CodeLogician extension in the sidebar.
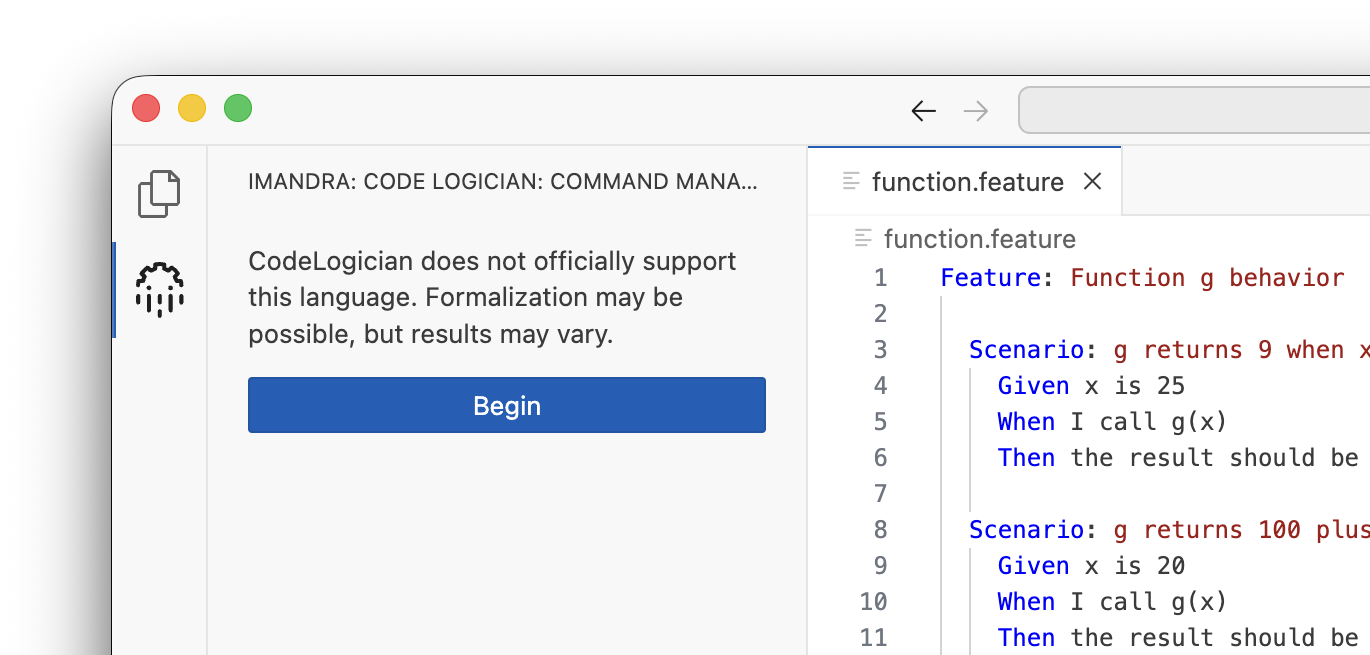
Unsupported languages
Formalization may be possible for languages that CodeLogician does not officially support, but results may vary. Select begin to acknowledge this and continue with formalization.
Commands
CodeLogician provides various commands which can be added to a queue, which is then __ .
Most commands have prerequisites that must be satisfied before they can be used. For example, one must perform a region decomposition before test cases can be generated. The command selector marks commands whose prerequisites haven't been satisfied as unavailable.
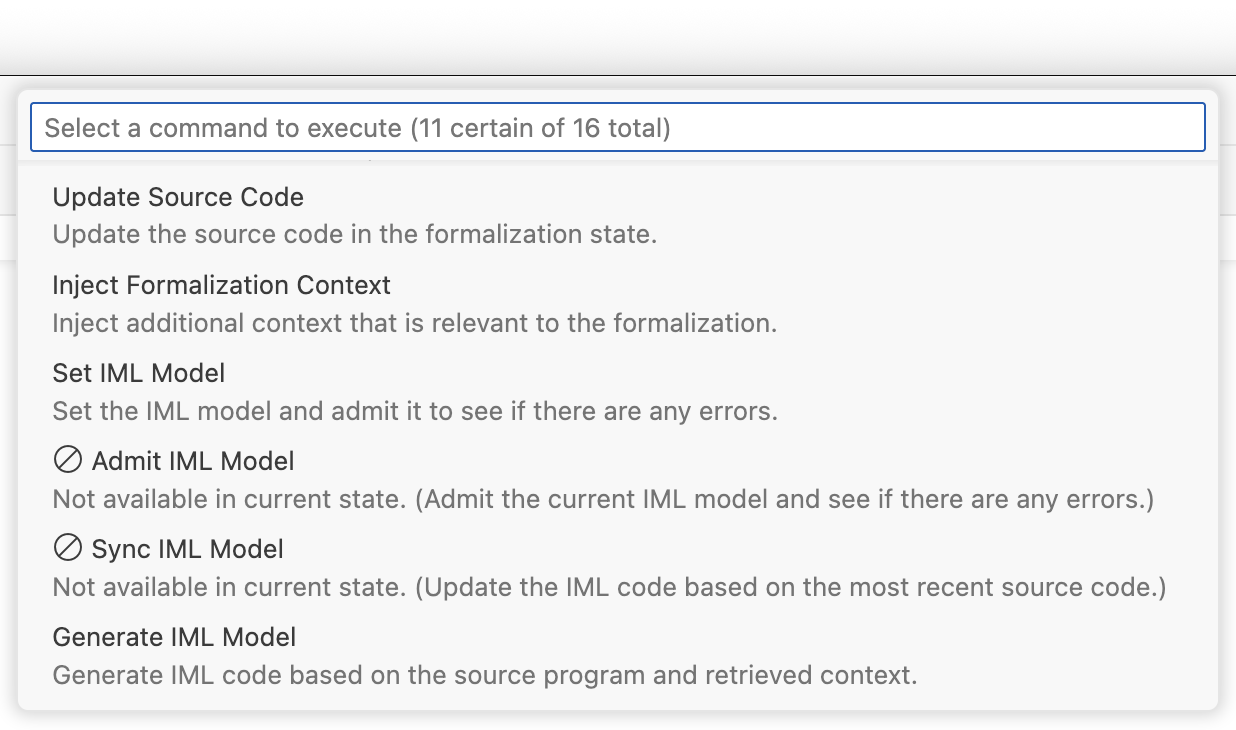
The Init State command is required always, so it is added to the start of the
queue automatically.
The Summary of Interactions, accessed via STATE VIEWERS view in the sidebar, displays the queue.
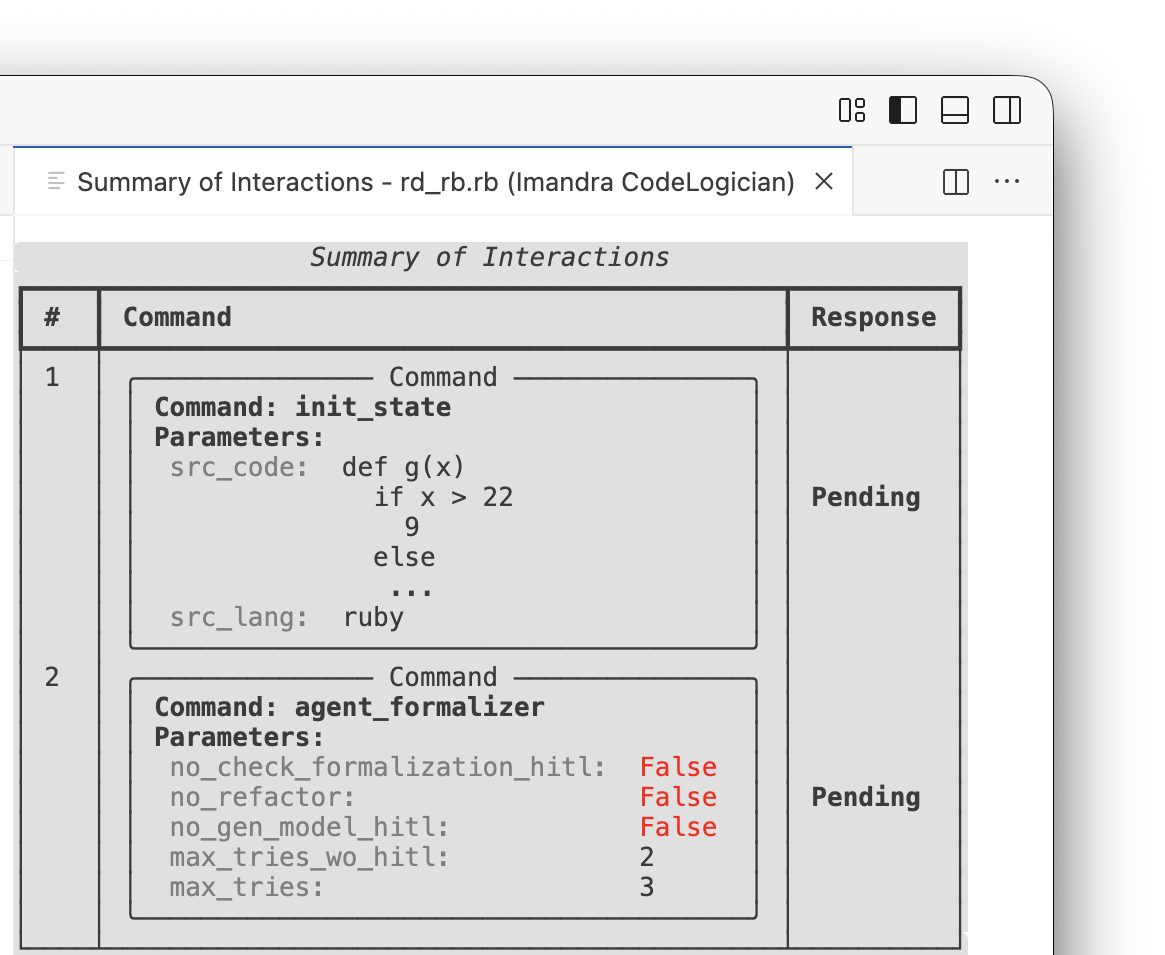
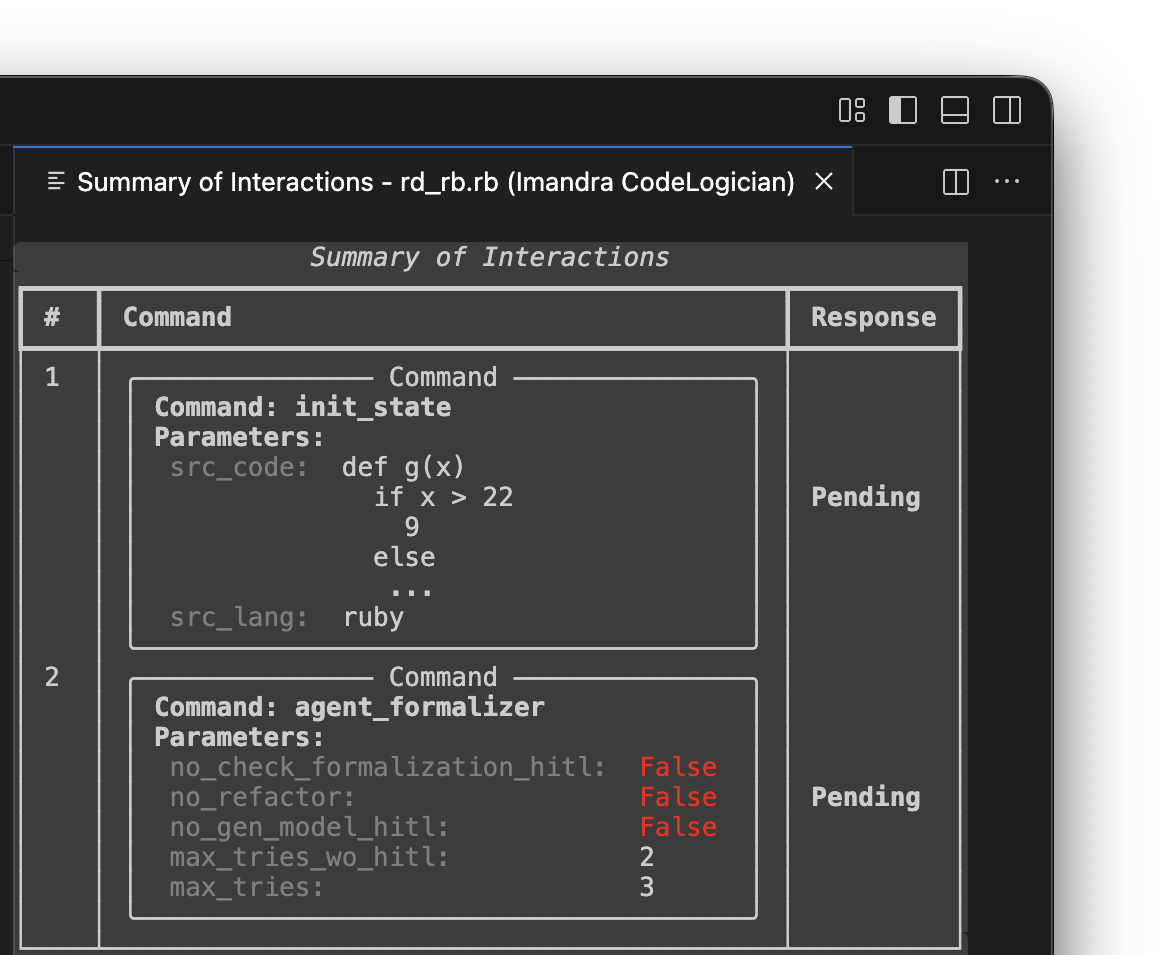
Run commands using Run pending commands. When commands conclude running, further tasks can be added to the queue.
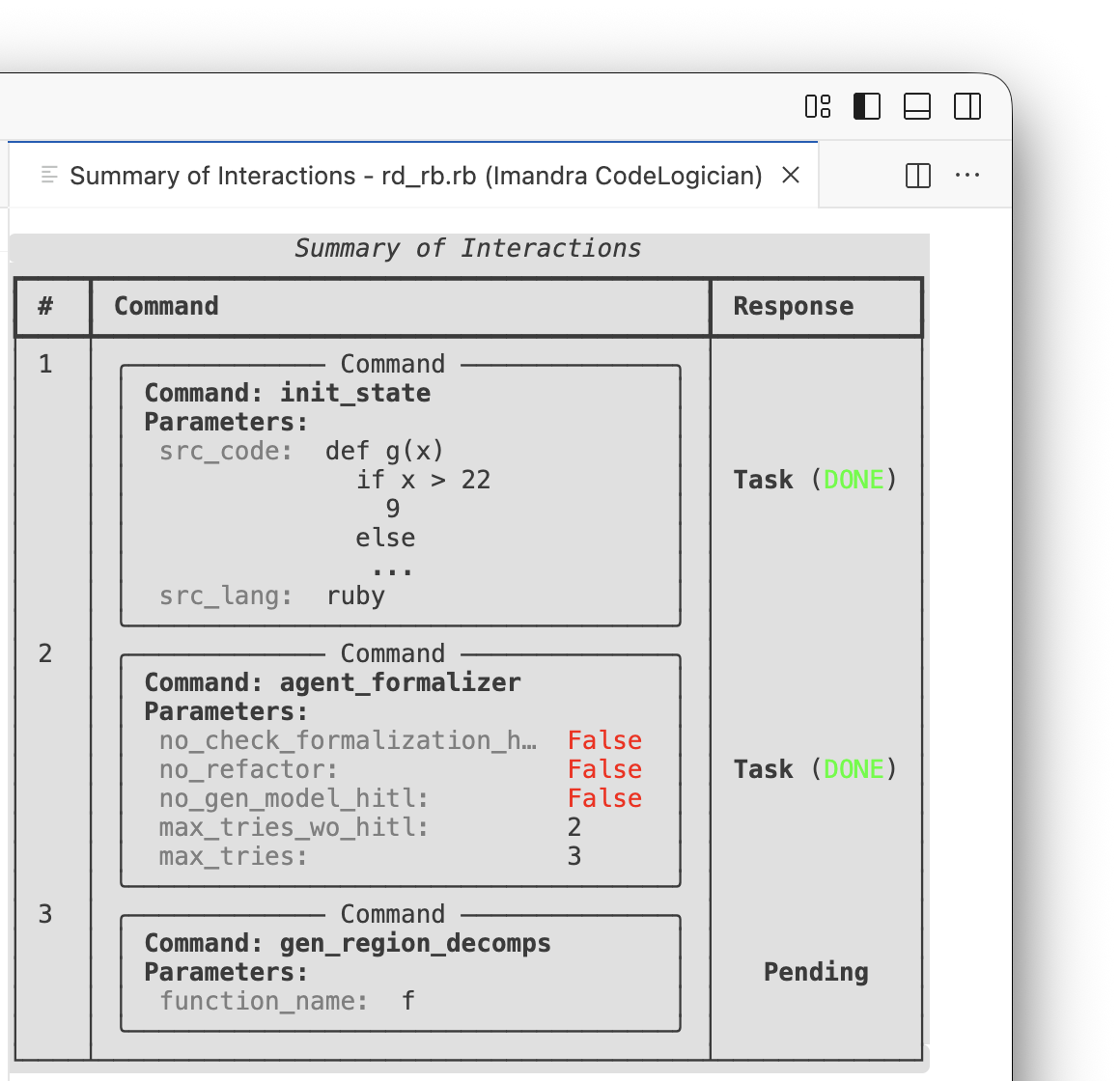

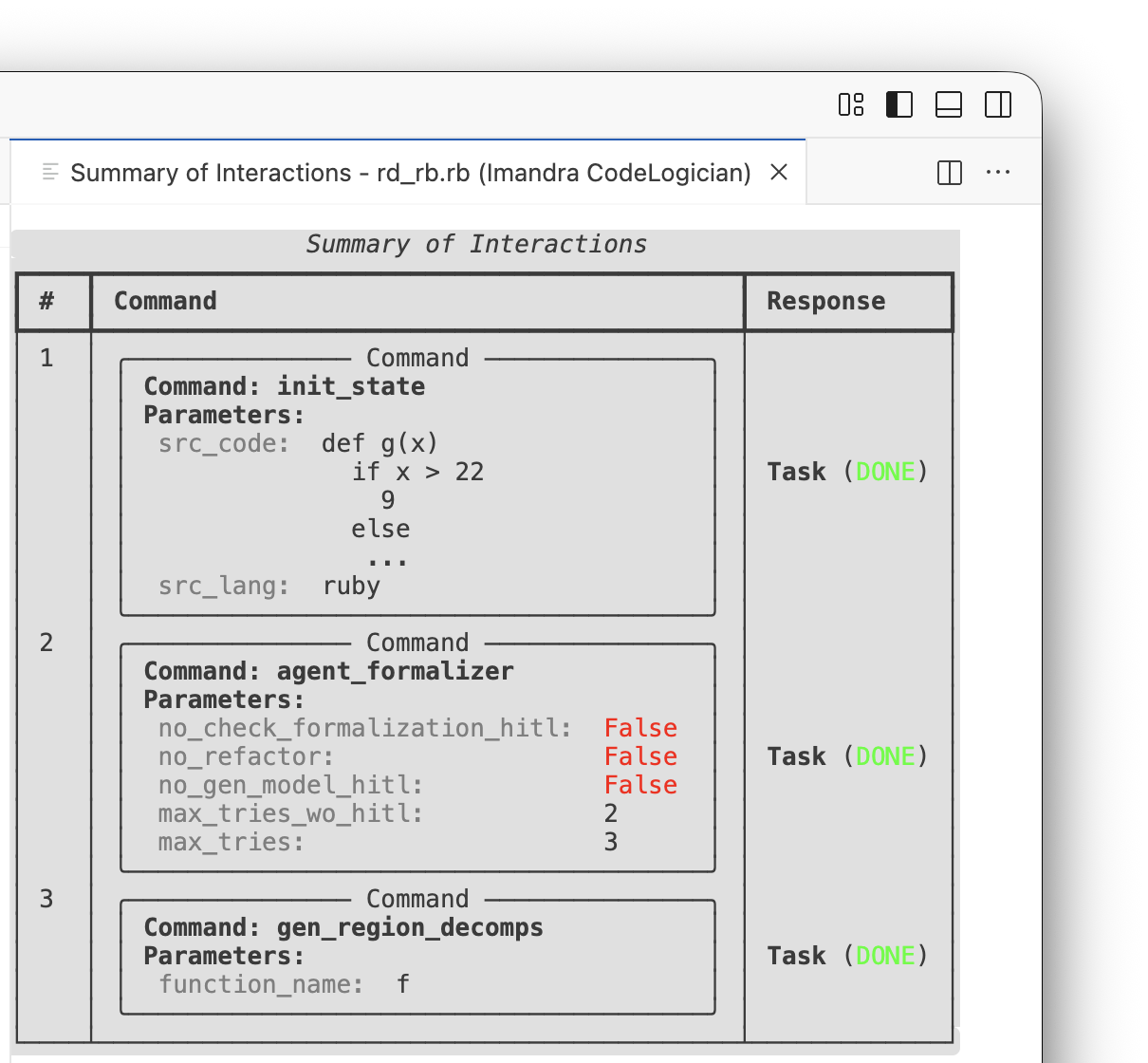
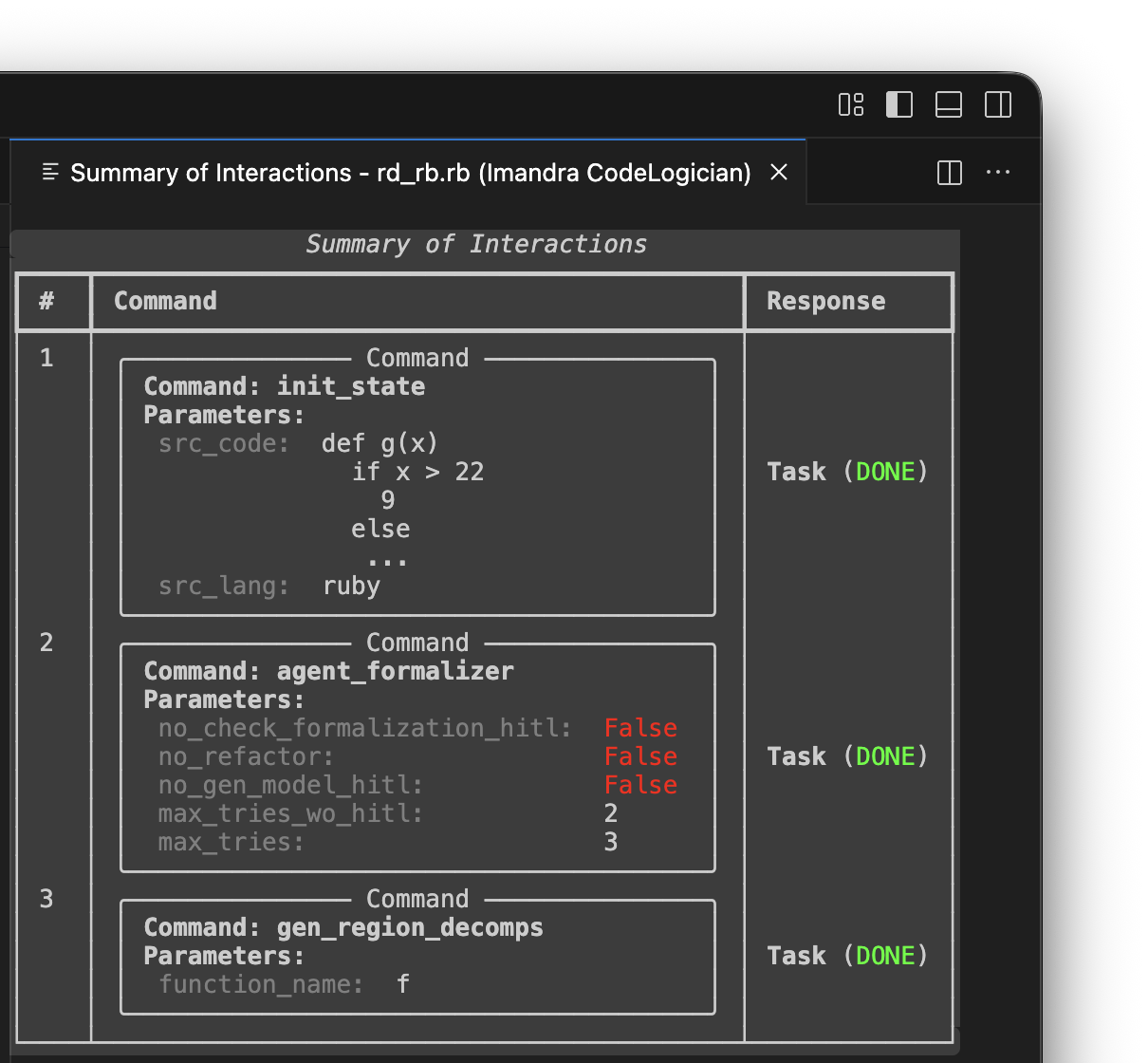
If a command was added by mistake, it can be removed from the queue using Delete command. Only pending commands can be removed. The Clear graph state option can be used to start from a clean slate, although it is not usually necessary.
IML
When formalizing, a formal IML model is created and saved in the code_logician/ subdirectory of the project.
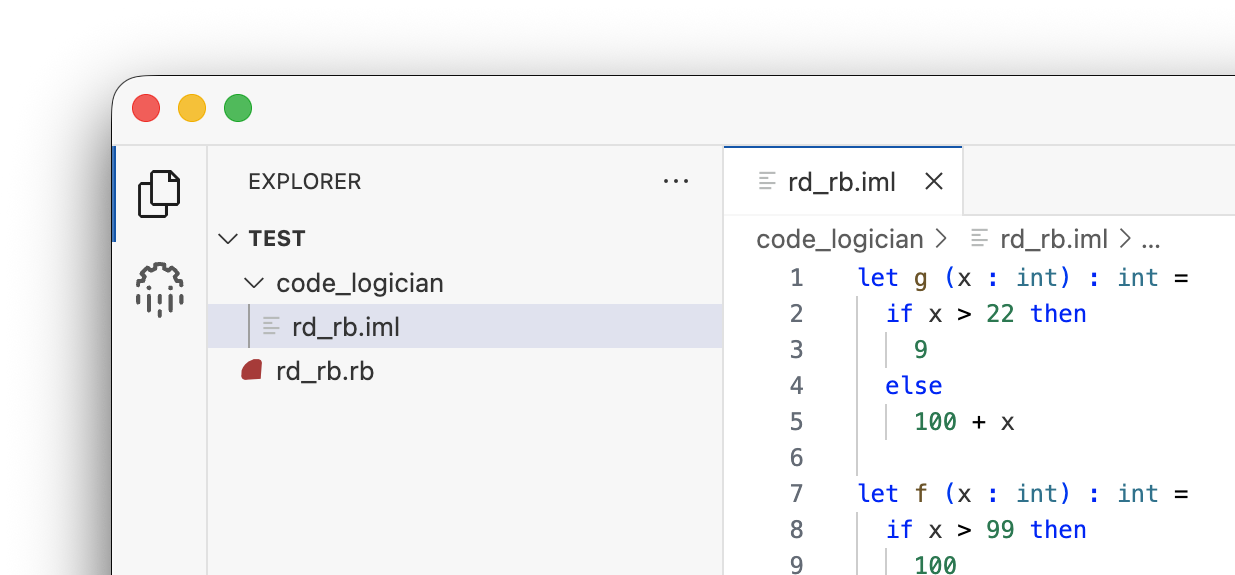
To update the source code after editing the IML model, first use the Set Model command, then Update Source Code.
Verification Goals
Generate verification goals by adding them to the source code as comments or submitting a VG description when adding the Generate Verification Goals command. An example follows.
Example
Source code
def g(x)
if x > 22
9
else
100 + x
end
end
def f(x)
if x > 99
100
elsif x > 23 && x < 70
89 + x
elsif x > 20
g(x) + 20
elsif x > -2
103
else
99
end
endIn this simple example, we use the following VG description when adding the Generate Verification Goals command:
Verify that f never returns a negative value
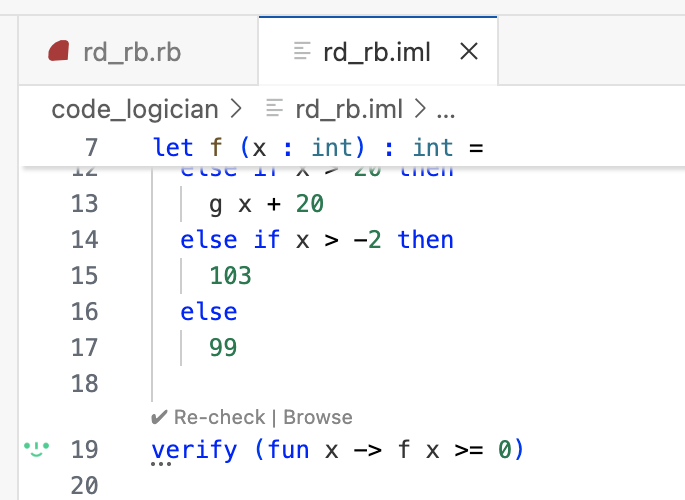
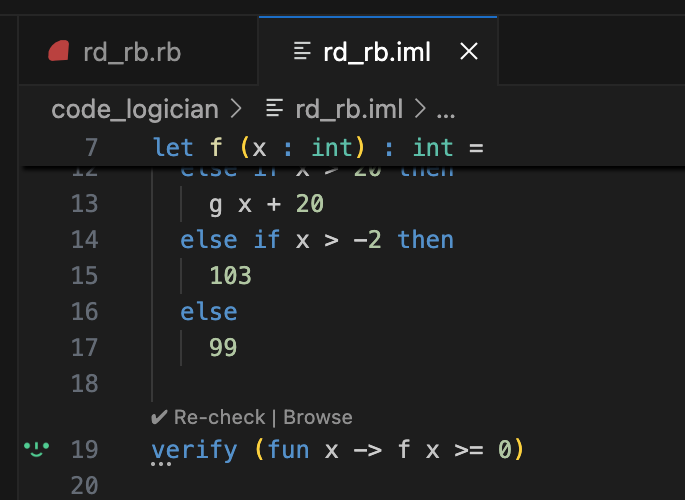
CodeLogician has appended the verification command to the IML model, and the ImandraX extension has checked it.
JSON
Formalization data, test cases, verification goals, and region decompositions can be exported as JSON. These are also saved in the code_logician/ subdirectory of the project.
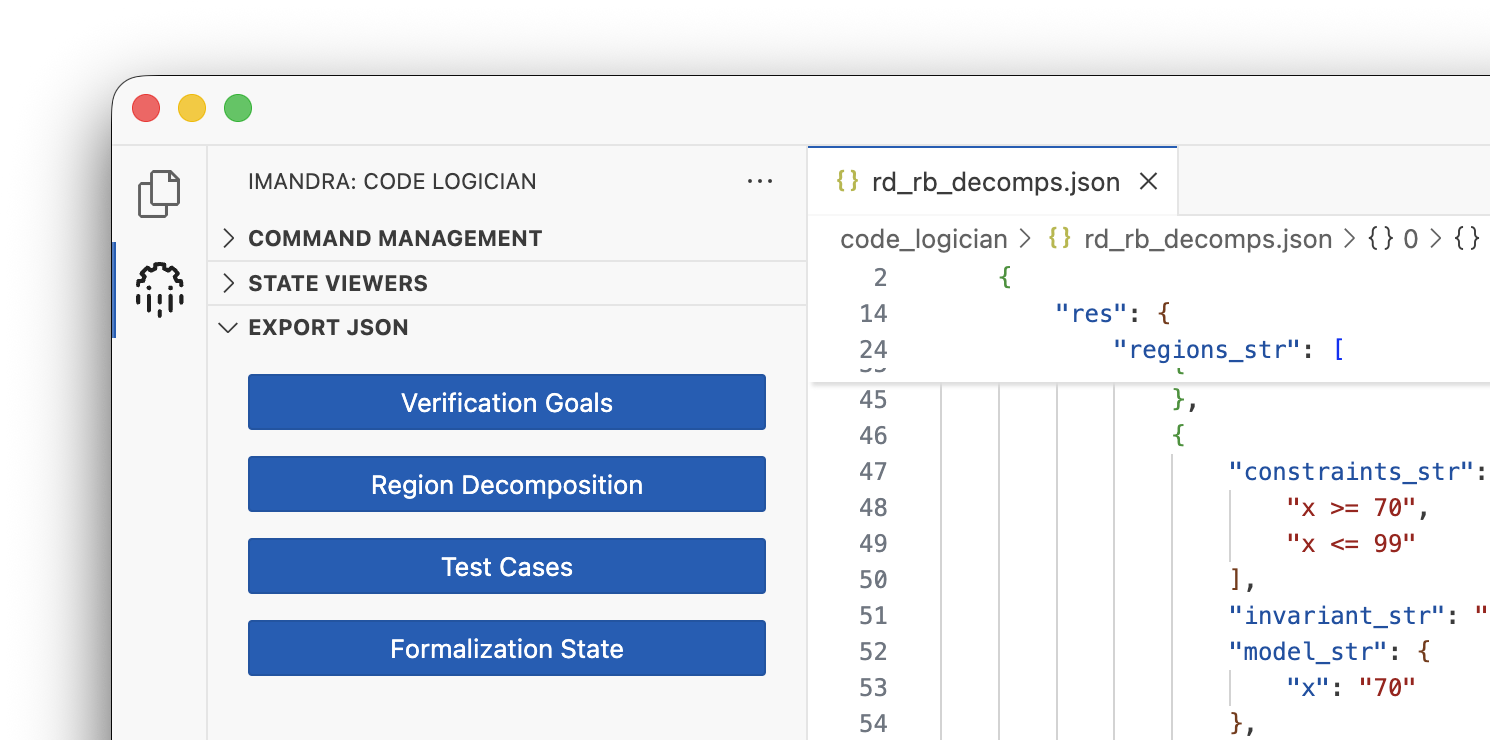
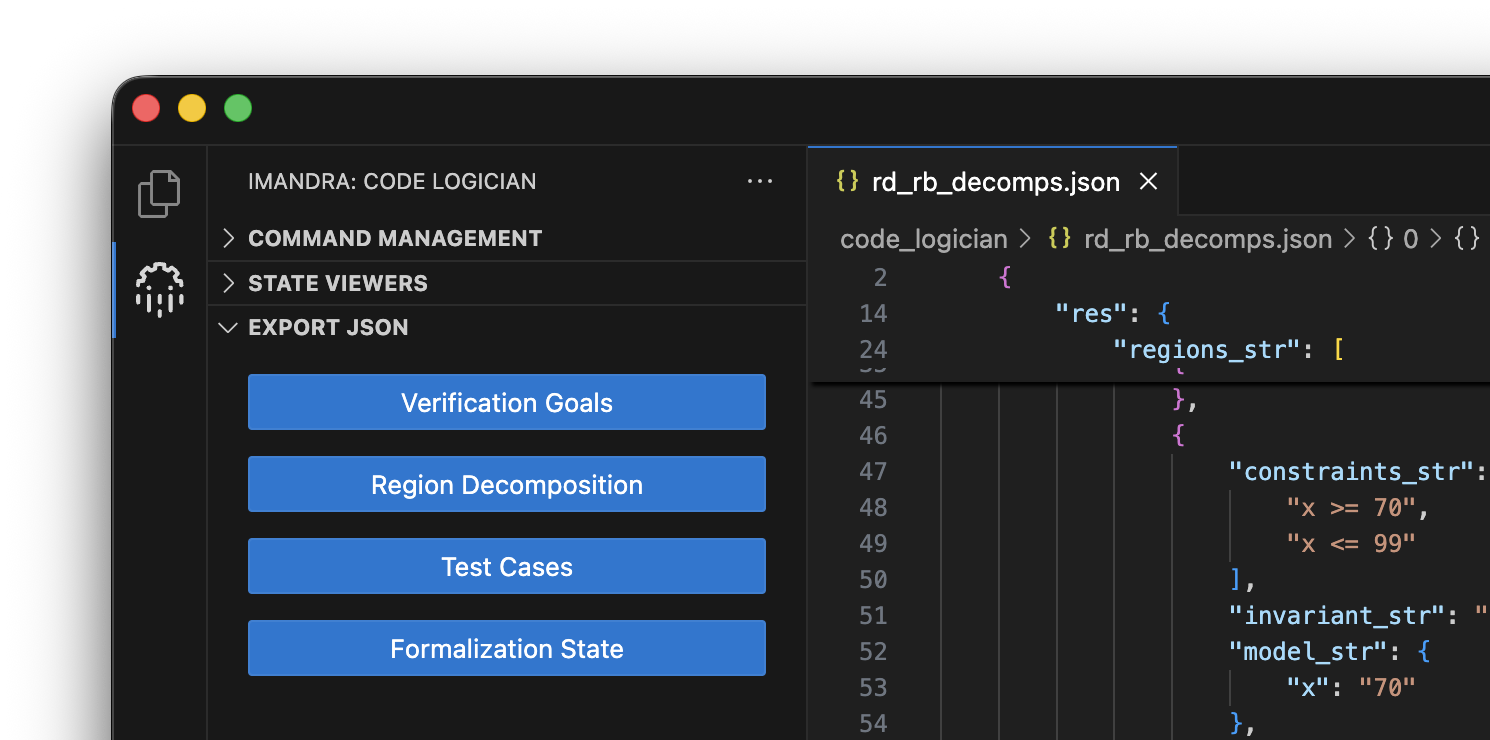
Configuration
The extension is configured through the VS Code settings.
API access
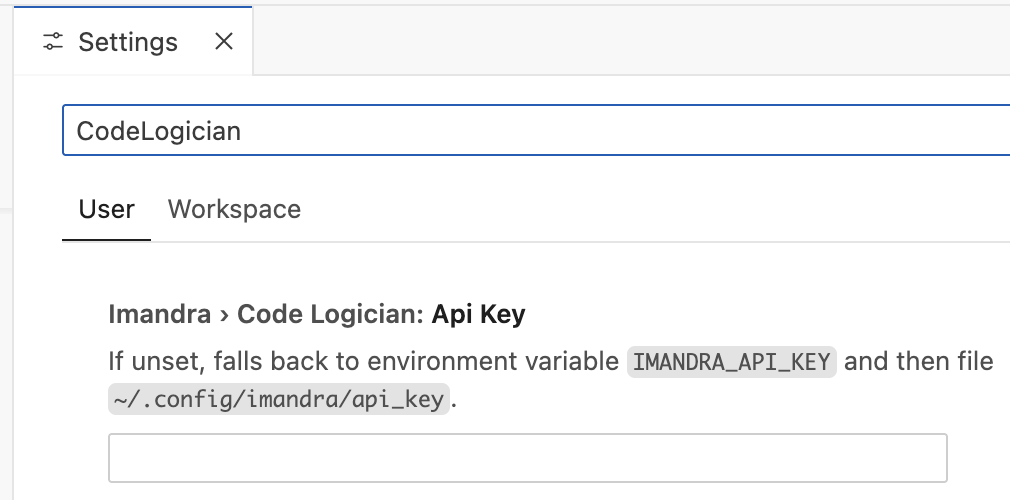
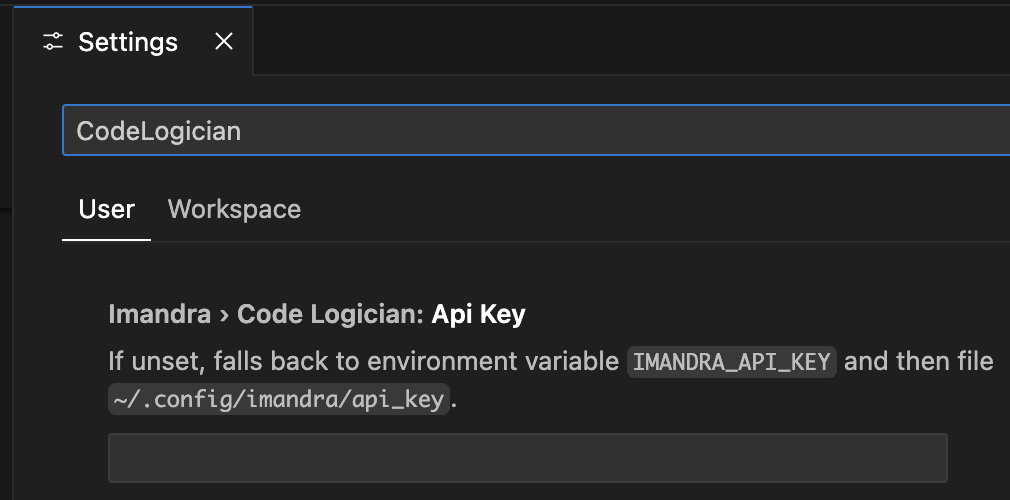
An API key is essential for the extension to work. Get one by signing up for a free Imandra Universe account.
Set your API key in the VS Code settings by searching for imandra.codeLogician.apiKey.
Debug logging
Debug logging can be using imandra.codeLogician.enableDebugLogging in VS Code settings.
State view scaling
The width of the content of the state viewer webview can be adjusted if it is not scaling correctly. Search for imandra.codeLogician.webviewWidthDivisor in VS Code settings to modify.